NIS2 Directive: A Strategic Cybersecurity and Resilience Framework for European Organizations

Introduction — Why NIS2 Matters Now
The cybersecurity landscape in Europe has evolved rapidly. Nation-state threats, supply chain attacks, and critical infrastructure compromises have highlighted the need for stronger and more harmonized resilience requirements across the European Union.
To address these challenges, the European Union adopted the NIS2 Directive (Directive (EU) 2022/2555) — an updated and expanded version of the original NIS Directive — with the objective of enhancing cybersecurity resilience, incident reporting, and risk management across a broad range of sectors deemed essential or important to the functioning of the economy and society.
NIS2 introduces more rigorous requirements, clearer supervisory expectations, and stronger enforcement mechanisms, signaling a shift toward regulatory maturity in cybersecurity.
What Is the NIS2 Directive?
The NIS2 Directive (Network and Information Systems Directive 2) is an EU-wide legislative framework that sets mandatory cybersecurity risk-management and incident-reporting rules for organizations operating in critical sectors. It replaces the original NIS Directive to address evolving threats, technology convergence, and cross-border interdependencies.
NIS2 aims to:
- Harmonize cybersecurity requirements across EU Member States.
- Reduce fragmentation in national implementations.
- Increase accountability at the board and management level.
- Strengthen cooperation between public authorities.
- Improve incident detection, reporting, and response.
The Directive moves beyond voluntary guidance to establish legal obligations that are enforceable with sanctions, fines, and corrective measures.
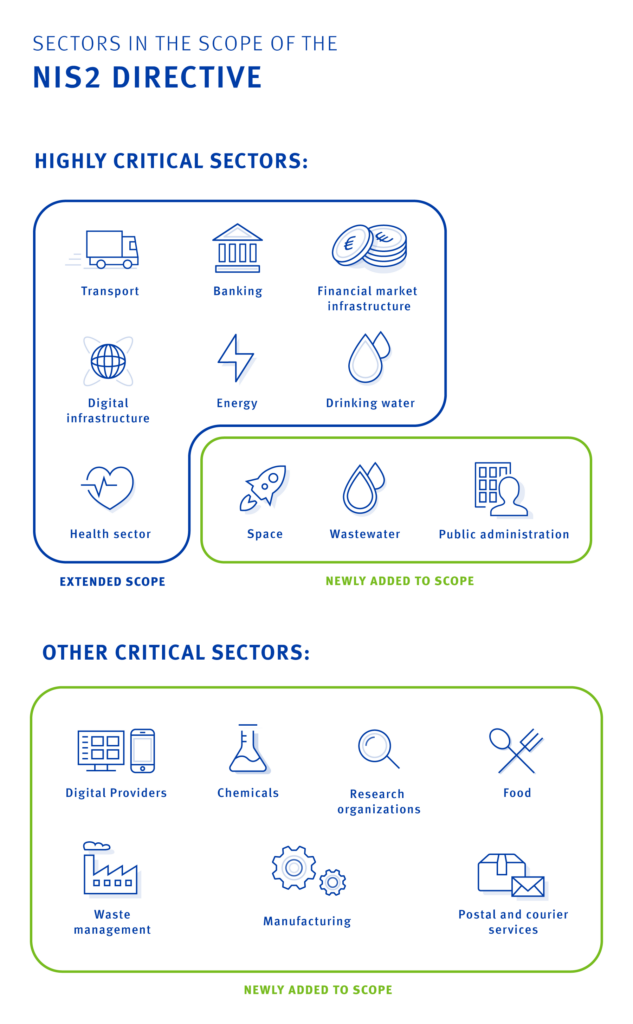
Scope and Applicability of NIS2
NIS2 applies to two broad categories of entities:
- Essential Entities (EEs):
– Entities whose disruption would significantly affect societal functions or economic stability (e.g., energy, transport, banking, healthcare, digital infrastructure). - Important Entities (IEs):
– Entities in sectors with medium to high impact (e.g., food supply, waste management, certain digital services).
Unlike the original NIS Directive, NIS2 establishes clearer thresholds and criteria for inclusion, reducing ambiguity about which organizations fall under its scope.
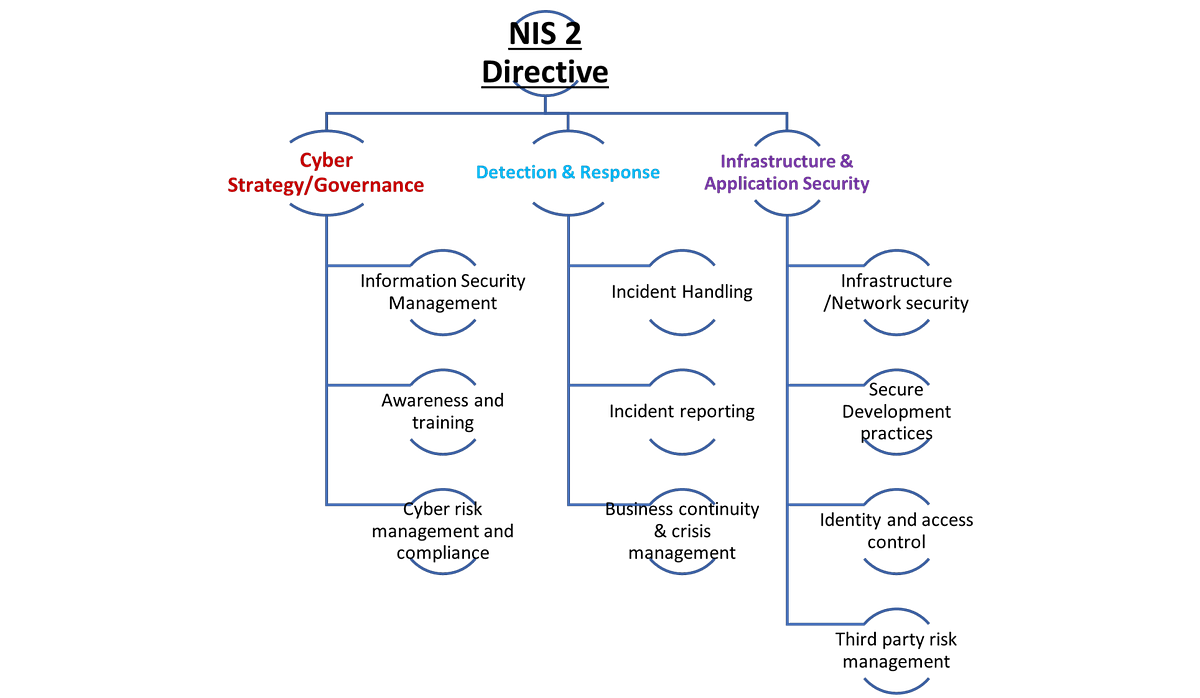
Key Requirements Under NIS2
NIS2 elevates cybersecurity expectations by imposing a set of mandatory obligations across all covered entities. Key requirements include:
Risk Management and Security Measures
Organizations must implement appropriate and proportionate technical, organizational, and governance measures to manage cybersecurity risk. These cover:
- Asset management (hardware, software, data).
- Access control and identity management.
- Incident prevention and detection (monitoring, logging).
- Business continuity and disaster recovery planning.
- Supply chain and third-party risk management.
Incident Reporting
NIS2 mandates mandatory incident notification with strict timelines:
- Initial report within 24 hours of becoming aware of an incident with major impact.
- Detailed report within 72 hours or as soon as feasible, including root cause analysis and mitigation status.
Governance and Accountability
Senior management must be accountable for cybersecurity governance, including approval of policies, oversight of risk management, and resource allocation. NIS2 explicitly requires board-level engagement and regular reporting on cybersecurity performance.
Supply Chain and Supplier Security
Organizations must assess and manage cyber risks in their supply chains and vendor ecosystems. NIS2 introduces supplier security considerations as part of core risk management responsibilities.
Cooperation and Information Sharing
NIS2 strengthens cooperation between national authorities and EU bodies. Entities subject to NIS2 may participate in information sharing and early warning networks, contributing to collective situational awareness and cross-border responses.
Why NIS2 Matters for Corporations
Regulatory Certainty and Harmonization
Before NIS2, cybersecurity requirements varied significantly across EU Member States, creating compliance uncertainty for multinational organizations. NIS2 harmonizes key obligations, reducing legal fragmentation and enabling more consistent implementation of security risk programs.
Enhanced Risk Management Discipline
NIS2’s risk-management focus pushes organizations to adopt enterprise-wide cybersecurity governance, formal risk assessments, documented controls, and measurable performance indicators — moving cybersecurity beyond the IT department to board and executive levels.
Incident Preparedness and Response Capabilities
Mandatory incident reporting and post-incident analysis under NIS2 accelerate detection and response activities. Organizations that align with NIS2 are better positioned to detect, contain, and recover from incidents, reducing operational disruption and cascading impacts.
Supply Chain Resilience
By requiring due diligence of third-party service providers and suppliers, NIS2 incentivizes stronger vendor security management practices, which enhances systemic resilience across interconnected digital ecosystems.
Implementing NIS2 in Practice
Step 1: Scoping and Gap Analysis
Organizations should begin by determining whether they qualify as an Essential or Important Entity under NIS2. This involves analyzing sector, service criticality, and size thresholds.
A gap analysis compares current security controls and risk management processes against NIS2 obligations to identify areas needing reinforcement.
Step 2: Governance and Risk Management Framework
Development of a governance structure with defined roles, responsibilities, and accountability is essential. Risk assessments should be formalized, documented, and revisited periodically.
Step 3: Incident Management and Reporting Design
Entities must establish incident detection, classification, and reporting workflows aligned with NIS2 timelines and documentation requirements.
Step 4: Supply Chain and Third-Party Risk Controls
Assessments and contractual security requirements should be incorporated into procurement and vendor lifecycle processes.
Step 5: Capability Building and Monitoring
Investment in cybersecurity monitoring tools, logging infrastructure, and performance measurement capabilities enables ongoing compliance, trend analysis, and management reporting.
Key Benefits of NIS2 Compliance
- Stronger cybersecurity posture across critical functions
- Reduced compliance complexity through harmonization
- Faster incident detection and response
- Improved board-level oversight and accountability
- Enhanced resilience across supply chains and ecosystems
By encouraging integrated risk management and cross-functional coordination, NIS2 supports both regulatory compliance and strategic operational resilience.
NIS2 and Related Frameworks
NIS2 complements other cybersecurity standards and regulatory frameworks, including:
- ISO/IEC 27001, as a risk-based security management system.
- DORA (Digital Operational Resilience Act), with aligned objectives for ICT risk and incident handling in financial services.
- GDPR, for data protection obligations related to security and breach notification.
Organizations can map NIS2 requirements to these existing frameworks to create cohesive security and compliance programs.
Conclusion — NIS2 as a Catalyst for Cyber Resilience
The NIS2 Directive represents a significant evolution in EU cybersecurity regulation. By establishing clear, harmonized, and enforceable requirements, NIS2 elevates cybersecurity from a technical function to an enterprise governance imperative.
For corporations operating within the EU — and for organizations supporting EU operations — aligning with NIS2 is not just about compliance. It is about building resilient systems, accountable governance, and trusted services in an era where cyber risk is both persistent and strategic.



